(Credit: Feichen Yang)
A cartilage-mimicking material created by researchers at Duke University may one day allow surgeons to 3D print replacement knee parts that are custom-shaped to each patient’s anatomy.
Human knees come with a pair of built-in shock absorbers called the menisci. These ear-shaped hunks of cartilage, nestled between the thigh and shin bones, cushion every step we take. But a lifetime of wear-and-tear — or a single wrong step during a game of soccer or tennis — can permanently damage these key supports, leading to pain and an increased risk of developing arthritis.
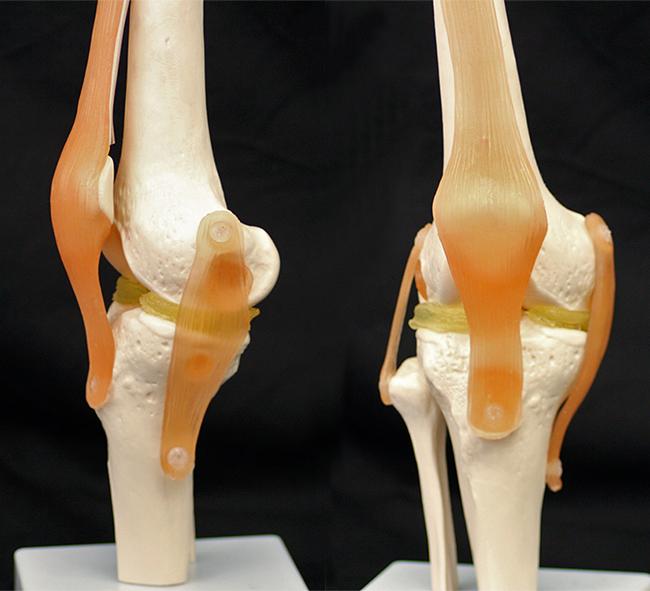
The hydrogel-based material the researchers developed is the first to match human cartilage in strength and elasticity while also remaining 3D-printable and stable inside the body. To demonstrate how it might work, the researchers used a $300 3D printer to create custom menisci for a plastic model of a knee.
“We’ve made it very easy now for anyone to print something that is pretty close in its mechanical properties to cartilage, in a relatively simple and inexpensive process,” says Benjamin Wiley, an associate professor of chemistry at Duke and author on the paper, which appears online in ACS Biomaterials Science and Engineering.
After we reach adulthood, the meniscus has limited ability to heal on its own. Surgeons can attempt to repair a torn or damaged meniscus, but often it must be partially or completely removed. Available implants either do not match the strength and elasticity of the original cartilage, or are not biocompatible, meaning they do not support the growth of cells to encourage healing around the site.
Recently, materials called hydrogels have been gaining traction as a replacement for lost cartilage. Hydrogels are biocompatible and share a very similar molecular structure to cartilage: if you zoom in on either, you’ll find a web of long string-like molecules with water molecules wedged into the gaps.
But researchers have struggled to create recipes for synthetic hydrogels that are equal in strength to human cartilage or that are 3D-printable.
“The current gels that are available are really not as strong as human tissues, and generally, when they come out of a printer nozzle they don’t stay put — they will run all over the place, because they are mostly water,” Wiley says.
Feichen Yang, a graduate student in Wiley’s lab and author on the paper, experimented with mixing together two different types of hydrogels — one stiffer and stronger, and the other softer and stretchier — to create what is called a double-network hydrogel.
“The two networks are woven into each other,” Yang says. “And that makes the whole material extremely strong.”
By changing the relative amounts of the two hydrogels, Yang could adjust the strength and elasticity of the mixture to arrive at a formula that best matches that of human cartilage.
He also mixed in a special ingredient, a nanoparticle clay, to make the mock-cartilage 3D-printable. With the addition of the clay, the hydrogel flows like water when placed under shear stress, such as when being squeezed through a small needle. But as soon as the stress is gone, the hydrogel immediately hardens into its printed shape.
3-D printing of other custom-shaped implants, including hip replacements, cranial plates, and even spinal vertebrae, is already practiced in orthopedic surgery. These custom implants are based on virtual 3D models of a patient’s anatomy, which can be obtained from computer tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans.
Meniscus implants could also benefit from 3D printing’s ability to create customized and complex shapes, the researchers say. “Shape is a huge deal for the meniscus,” Wiley says. “This thing is under a lot of pressure, and if it doesn’t fit you perfectly it could potentially slide out, or be debilitating or painful.”
“A meniscus is not a homogenous material,” Yang added. “The middle is stiffer, And the outside is a bit softer. Multi-material 3D printers let you print different materials in different layers, but with a traditional mold you can only use one material.”
In a simple demonstration, Yang took a CT scan of a plastic model of a knee and used the information from the scan to 3D print new menisci using his double network hydrogel. The whole process, from scan to finished meniscus, took only about a day, he says.
“This is really a young field, just starting out,” Wiley says. “I hope that demonstrating the ease with which this can be done will help get a lot of other people interested in making more realistic printable hydrogels with mechanical properties that are even closer to human tissue.”