Physicians currently spend a lot of time writing notes about patients and inserting them into electronic health record (EHR) systems. According to a 2016 study, doctors spend approximately two hours on administrative work for every hour spent with a patient. Thanks to cutting-edge artificial intelligence tools, this note-writing process could soon become automated, helping doctors to better manage their shifts and relieving them from this tedious task.
Peter Liu, a researcher at Google Brain, has recently developed a new language modeling task that can predict the content of new notes by analyzing patient medical records, which include data such as demographics, laboratory measurements, medications and past notes. In his study, pre-published on arXiv, he trained generative models using the MIMIC-III (Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care) EHR dataset, and then compared the notes generated by the models with real notes from the dataset.
Commonly adopted methods to reduce the time that clinicians spend on note-taking include the use of dictation services and the employment of assistants who can write up notes for them. Artificial intelligence tools could help to tackle this issue, reducing costs spent on additional staff and resources.
“Assistive-writing features for notes, such as auto-completion or error-checking, benefit from language models,” Liu writes in his paper. “The stronger the model, the more effective such features would likely be. Thus, the focus of this paper is in building language models for clinical notes.”
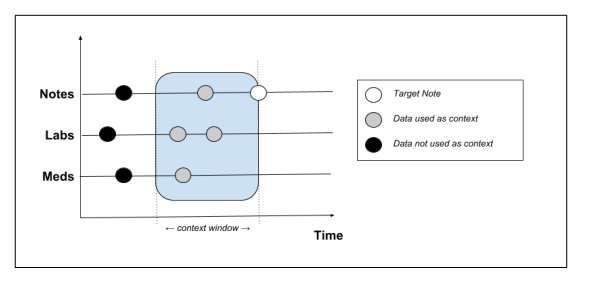
Figure 2: Schematic showing how raw data is transformed to model training data. Credit: Peter Liu
Liu employed two language models: the first is called transformer architecture, and was introduced in a study published last year in the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems journal. As this model performs better with shorter texts, such as individual sentences, he also tested a recently introduced transformer-based model, called transformer with memory-compressed attention (T-DMCA), which was found to be more effective for longer sequences.
He trained these models on the MIMIC-III dataset, containing de-identified EHR of 39,597 patients from the intensive-care unit of a tertiary care hospital. This is currently the most comprehensive EHR dataset that is publicly available and can be easily accessed online.
“We have introduced a new language modeling task for clinical notes based on HER data and showed how to represent the multi-modal data context to the model,” Liu explained in his paper. “We proposed evaluation metrics for the task and presented encouraging results showing the predictive power of such models.”
The models were effectively able to predict a lot of the content of physicians’ notes. In future, they could aid the development of more sophisticated spell-checking and auto-complete features. These features could be then integrated into tools that assist clinicians in completing administrative work. While the results of this study are promising, some challenges still need to be overcome before the models can be employed on a larger scale.
“In many cases, the maximum context provided by the EHR is insufficient to fully predict the note,” Liu explains in his paper. “The most obvious case is the lack of imaging data in MIMIC-III for radiology reports. For non-imaging notes we also lack information about the latest patient-provider interactions. Future work could attempt to augment the note context with data beyond the EHR, e.g. imaging data, or transcripts of patient-doctor interactions. Although we discussed error correction and auto-complete features in EHR software, their effects on user productivity were not measured in the clinical context, which we leave as future work.”




