Care for critically-ill patients with shock could be improved, it is hoped, after the first successful testing by University of Oxford scientists of a new machine to record oxygen consumption in real time.
The new technology has arisen through a collaboration between Professor Peter Robbins in the Department of Physiology, Anatomy and Genetics and Professors Grant Ritchie and Gus Hancock in the Department of Chemistry. It combines laser spectroscopy and precise flow measurement of breath in a single medical device which fits into a standard ventilation tube.
The work has received public funding from the NIHR Oxford Biomedical Research Center and the Medical Research Council.
“This is the culmination of many years of development and it has finally come to fruition,” said professor Peter Robbins, who is directing the research. “It is exciting for us to be able to offer something to doctors that has the potential to improve significantly the care of very sick patients.”
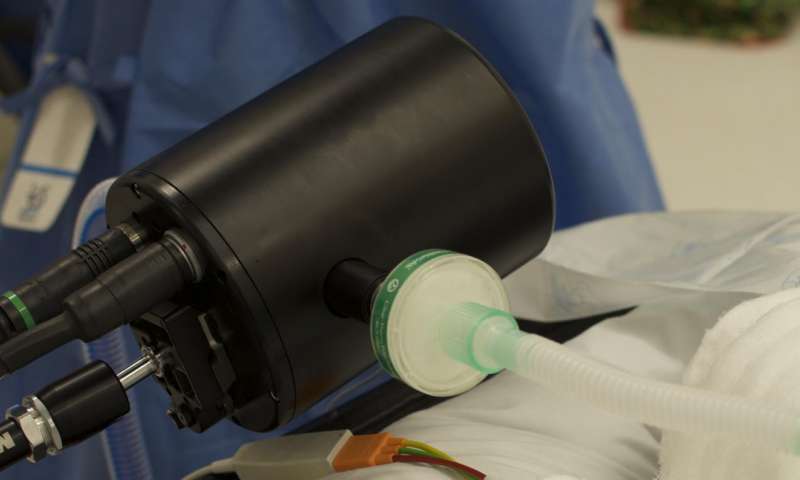
The University of Oxford has developed a new machine, called the Molecular Flow Sensor (MFS), to record oxygen consumption in real time for critically ill patients with shock. (Credit: University of Oxford)
Patients in shock suffer a lack of oxygen throughout the body, causing many of their organs to deteriorate and eventually even stop working altogether.The possible underlying causes of shock include heart attack, hemorrhage, and sepsis. Common treatments include drugs, oxygen, and blood transfusions. Doctors do not at present have any direct way of measuring how much oxygen is being used by the body, making it difficult for them to judge which treatments are likely to be most beneficial.
Tests in healthy volunteers and in patients having anesthetics at Oxford’s John Radcliffe Hospital indicate the precision of the device is better than anything previously achieved. The results are published today in Science Advances.
The device is now being used as part of a further study in the Intensive Care units within Oxford University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, which runs the John Radcliffe Hospital.




