
Nanowire extraction allowed many microRNAs to be compared at once using urine samples collected from patients. Expression of each microRNA is shown as low/downregulated (blue), intermediate (black), or high/upregulated (yellow). The analysis reveals unique patterns of expression for groups of microRNAs when comparing healthy donors (?) with cancer patients (+). (Credit: Takao Yasui)
Cells communicate through a number of mechanisms. Some are well-known: In animals, for example, predatory threats can drive the release of norepinephrine, a hormone that travels through the bloodstream and triggers heart and muscle cells to initiate a “fight-or-flight” response.
A far less familiar mode of cellular transport is the extracellular vesicle (EV). EVs can be thought of as small “chunks” of a cell that are able to pinch off and circulate throughout the body to deliver messenger cargo to other cells. These messengers have become increasingly recognized as crucial mediators of cell-to-cell communication.
In a new study reported in Science Advances, researchers at Nagoya University have developed a novel medical device that can efficiently capture these EVs, and potentially use them to screen for cancer. “EVs are potentially useful as clinical markers. The composition of the molecules contained in an EV may provide a diagnostic signature for certain diseases,” says lead author Takao Yasui. “The ongoing challenge for physicians in any field is to find a non-invasive diagnostic tool that allows them to monitor their patients on a regular basis—for example, a simple urine test.”
Among the many molecules EVs have been found to harbor are microRNAs, which are short pieces of ribonucleic acid that play diverse roles in normal cellular biology. Critically, the presence of certain microRNAs in urine might serve as a red flag for serious conditions such as bladder and prostate cancer. While this important cargo could therefore theoretically aid physicians in cancer diagnoses, there are still many technological hurdles. One such hurdle is finding a feasible method to capture EVs in sufficient quantities to analyze them in a routine clinical setting.
“The content of EVs in urine is extremely low, at less than 0.01 percent of the total fluid volume. This is a major barrier to their diagnostic utility,” Yasui notes. “Our solution was to embed zinc oxide nanowires into a specialized polymer to create a material that we believed would be highly efficient at capturing these vesicles. Our findings suggest that the device is indeed quite efficient. We obtained a collection rate of over 99 percent, surpassing ultracentrifugation as well as other methods that are currently being used in the field.”
To test the practicality of their device, the research team compared the microRNAs of EVs isolated from healthy patients with those isolated from patients who were already diagnosed with bladder, prostate, and other forms of cancer. Notably, their technique required only 1 milliliter of urine—far more than the typical “deposit” provided during a routine checkup—and found a substantially greater number and different types of microRNAs compared with the standard ultracentrifugation approach.
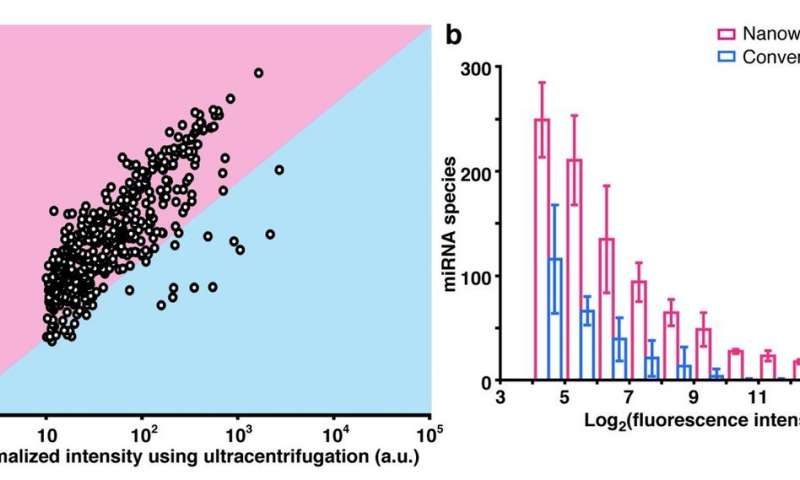
Comparison of microRNA extraction using nanowires versus conventional collection. (a) Scatterplot comparing normalized intensities of microRNAs extracted with the nanowire device versus conventional collection by ultracentrifugation. (b) Histogram showing the frequency of microRNA species at different fluorescent intensities collected by nanowires (red) and ultracentrifugation (blue). Both the scatterplot and histogram analyses show a notably greater abundance of extracted microRNAs using the nanowire technology. (Credit: Takao Yasui)
“Finding a specific, reproducible marker to help confirm a cancer diagnosis is difficult. This is especially true for microRNAs, which are a relatively new class of markers in the field,” co-author Yoshinobu Baba explains. “Sometimes finding just one reliable microRNA is considered a success. Using this approach, we were surprised to find that not just one, but whole combinations of microRNAs might be associated with different types of cancers. The findings are preliminary, of course, but we hope our device can help to lay the groundwork for easier ways to diagnose life-threatening diseases as early as possible.”




