The first human study of a pill designed to replace injections of biologics is today being announced by Rani Therapeutics, the inventor of the RaniPill capsule. The human study follows more than 100 animal studies testing the RaniPill capsule’s delivery of drugs such as insulin and Humira into the wall of the small intestine, where Rani has demonstrated 100 percent equivalence with injections.
The human study was conducted at a Clinical Research Organization (CRO) in Texas, under the Investigational Review Board (IRB) approval. There were two sub-groups, one cohort was fed and another fasted. Each subject swallowed a drug-free version of the RaniPill capsule. The study, which evaluated the RaniPill capsule platform, focused on safety and tolerability.
The results revealed no sensation of the capsule inflating or deploying, and the successful passing of the remnants. The RaniPill capsule was well-tolerated by both male and female adult subjects of similar BMI with no adverse events. The study showed similar intestinal deployment times for both fasted and fed subjects, indicating that food does not impact the RaniPill capsule’s performance. The next human study will be conducted later this year and will include a drug-filled resorbable needle.
This human study builds on Rani’s extensive preclinical porcine and canine studies conducted over five years with 10 molecules, including antibodies, peptides, and proteins. These studies in large animal models have demonstrated delivery equivalent to 3 milligrams (mg) or 3,000 micrograms (μg) of drug and bioavailability that is on par or better than subcutaneous injections. For context, 3,000 μg translates into 80 units of insulin. This dosage covers not only the pre-diabetic patient (300 micrograms) but also patients with more severe chronic diabetes conditions.
“This is a first-of-its-kind innovation that combines a range of disciplines from engineering, chemistry and materials science to anatomy, physiology, and biochemistry to convert injectable drugs into pills,” says Mir Imran, Rani’s Chairman and CEO. “The safety and tolerability of the RaniPill capsule in this first human study give us confidence in our platform as we prepare for human testing of the RaniPill capsule with Octreotide (a drug for the treatment of acromegaly) in the coming months.”
Rani’s extensive intellectual property portfolio, which includes over 150 patent applications filed and more than 50 patents issued in the U.S., covers important innovations for injecting into the gastrointestinal tract including the stomach and intestines.
Dennis Ausiello, M.D., Physician-in-Chief, Emeritus at Massachusetts General Hospital and Jackson Distinguished Professor of Clinical Medicine at Harvard Medical School and Rani board member adds, “The oral delivery of biologics is considered the holy grail of drug delivery. Rani has generated impressive bioavailability data in preclinical testing, while methodically and significantly de-risking its platform. With strong preclinical results and an extensive patent portfolio, Rani is poised to benefit patients across a range of therapeutic areas, including diabetes, psoriasis, Crohn’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis, hemophilia, among others.”
RaniPill Capsule’s Design
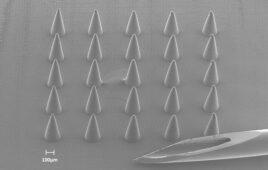
The RaniPill capsule has a special enteric coating that protects itself in the acidic environment of the stomach. When the capsule moves into the intestine and pH levels rise, the enteric coating dissolves and a chemical reaction takes place which inflates a balloon. The pressure in the balloon pushes the dissolvable microneedle filled with the drug into the intestinal wall. The uptake of the drug is immediate due to the highly vascularized intestinal wall. Because there are no sharp pain receptors in the intestine, the injection is painless. By comparison, subcutaneous injections can be painful, especially when patients have to inject themselves chronically.
The RaniPill capsule uses no metal, springs or other elements that the body cannot easily absorb or pass quickly. The company’s more than 100 preclinical studies, including the testing of more than 1,000 capsules in animal models, and its recent human study, have shown that large animals and humans are able to pass the remnants of the RaniPill capsule within one to four days.