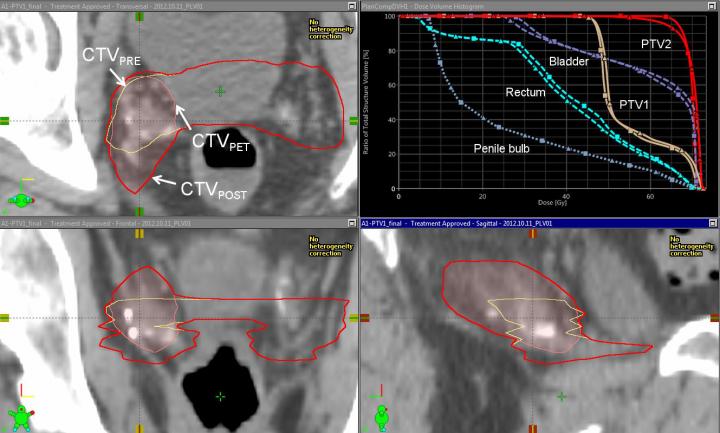
CTVPOST (red) = CTVPRE (yellow) union CTVPET (pink). Also shown (upper right corner) are the PRE (square) vs POST (triangle) dose volume histograms for PTV1, PTV2, rectum, bladder, and penile bulb, showing minimal impact on target coverage or organs at risk dose with the modified targets. (Credit: Ashesh B. Jani, MD, and David Schuster, MD, Emory University)
The featured clinical investigation article of the March 2017 issue of the Journal of Nuclear Medicinedemonstrates that the PET radiotracer fluciclovine (fluorine-18; F-18) can help guide and monitor targeted treatment for recurrent prostate cancer, allowing for individualized, targeted therapy.
“This is the first study of its kind demonstrating changes in post-surgery radiotherapy target design with advanced molecular imaging in recurrent prostate cancer, with no demonstrated increase in early radiotherapy side effects,” explains Ashesh B. Jani, MD, of the Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia.
According to the American Cancer Society, one in seven men will develop prostate cancer in his lifetime. In 2017, more than 161,000 new cases of prostate cancer are expected to be diagnosed in the U.S., and about 26,730 deaths from the disease are anticipated.
For the study, 96 patients were enrolled in a clinical trial of radiotherapy for recurrent prostate cancer after prostatectomy. All patients underwent initial treatment planning based on results from conventional abdominopelvic imaging (CT or MRI). Forty-five of the patients then underwent treatment-planning modification (better defining the tumor-targeted area) after additionally undergoing abdominopelvic F-18-fluciclovine PET/CT. No increase in toxicity was observed with this process.
The Emory researchers determined that the inclusion of F-18-fluciclovine PET information in the treatment planning process leads to significant differences in target volumes (the areas to receive radiotherapy). It did result in higher radiation dose delivered to the penile bulb, but no significant differences in bladder or rectal radiation dose or in acute genitourinary or gastrointestinal toxicity.
These are preliminary results in a three-year study, which hypothesizes that there will be an increase in disease-free survival for patients in the F-18-fluciclovine-modified treatment group over those in the standard treatment group.
This study could have implications beyond prostate cancer, Jani points out, “Our methodology is readily applicable to other novel imaging agents, and it may potentially facilitate improvement of cancer control outcomes.”




