DGIST announced that Professor Kyung-in Jang’s research team from the Department of Robotics Engineering succeeded in developing bio-signal measuring electrodes that can be mounted on Internet of Things (IoT) devices through joint research with a research team led by professor John Rogers of the University of Illinois, USA.
The bio-signal measuring electrodes developed by the research team can be easily mounted on IoT devices for health diagnosis, thus they can measure bio-signals such as brain waves and electrocardiograms without additional analysis and measurement equipment while not interfering or restricting human activities.
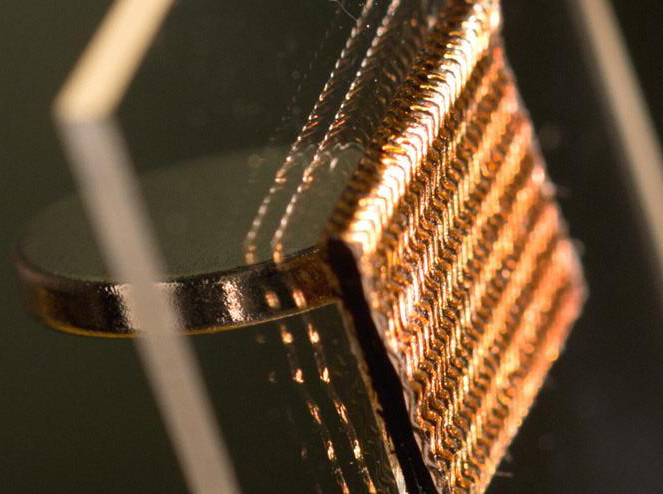
Optical image of bio-signal measurement electrode design developed by Professor Jang’s research team. The electrode generates such a large force that it holds the circular magnet located under the glass only by attraction (gravitation) of the magnetic field. (Credit:DGIST)
Conventional hydro-gel based electrodes required external analysis and measurement devices to measure bio-signals due to their pulpy gel forms, which made their attachment to and detachment from IoT devices instable. In addition, since these electrodes were wet-bonded to the skin, there have been disadvantages that the characteristics of the electrodes deteriorated or their performance decreased when the electrodes were dried in the air over a long period.
In contrast, the electrodes developed by Professor Kyung-in Jang can be easily interlocked as if they are a part of IoT devices for health diagnosis. Also, since they are composed only of polymer and metal materials, they have the advantage of there being no possibility of drying in the air.
The bio-signal measurement electrodes developed by the research team consist of a composite material in which a magnetic material is folded with a soft and adhesive polymer, with a conductive electrode material wrapped around the composite material. The conductive electrode material electrically connects the bottom surface touching the skin and the top surface touching the electrode of the IoT device.
Electrodes with this structure reacting to the magnetic field can be easily attached and detached by using the attraction that occurs between the magnet and the electrode mounted on the IoT devices. Then, through the conductive electrode materials that connect the skin and the electrode part of the IoT device, the electric signals generated on the skin can be directly transmitted to the IoT device for health diagnosis.
The research team succeeded in storing and analyzing brain waves (electroencephalogram, EEG), electrocardiograms (ECG), eye movements (electrooculogram, EOG), and limb movements and muscle contractions (electromyogram, EMG) of the wearer for a long period through an experiment in which IoT devices with the electrodes are attached to various parts of the human body.
The bio-signal measurement electrodes can measure the bioelectric signal generated from the skin without loss or noise by using the IoT platform, thus they are expected to be applicable to the medical and healthcare fields since they cannot only measure the electrical signals of the body, but also analyze various forms of bio-signals such as body temperature change, skin change, and in-body ion concentration change.
Professor Kyung-in Jang said, “We have secured the source technology that can diagnose the state of human health anytime and anywhere by combining bio-electrode technology with IoT platforms utilizing advanced high-tech composite materials. We will carry out subsequent research to make it applicable for diseases that require ongoing medical diagnosis such as diabetes, insomnia, and epilepsy, and to make it available to people in medically vulnerable areas such as remote mountainous and rural areas.”




