Compression Limiters are used to protect plastic components in bolted joints and maintain a threaded fastener’s clamp load by eliminating plastic creep. To function properly, bearing surface beneath the bolt’s head must extend over the Compression Limiter to contact the plastic component.
Assembly considerations
Several factors including speed and assembly method must be considered when determining the most cost effective solution for a specific application.

Various fastener combinations were manually assembled to determine approximate differences in efficiency.
Assembly Speed
Various fastener combinations were manually assembled to determine approximate differences in efficiency.
If this bearing surface is too small, the host component may not be retained by the bolt resulting in a poor joint.
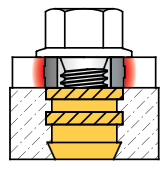
There are several methods to ensure sufficient bearing surface under the bolt’s head. These include the use of a flanged bolt, washer or headed Compression Limiter.

Assembly with a flanged bolt was the fastest, followed by that with a headed Compression Limiter, which must be oriented. As expected, the addition of a third component (the washer) significantly slowed the assembly process which required twice the assembly time.
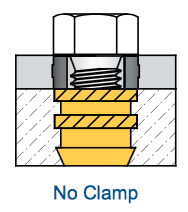
If this bearing surface is too small, the host component may not be retained by the bolt resulting in a poor joint.
Automating assembly
When an assembly is automated, it is imperative to ensure the design is as efficient as possible. The addition of a third component, such as a washer, may not be desirable when automating due to feeding and alignment challenges. Other common factors affecting efficiency include number of components and ease of orientation. All bolts, headed Compression Limiters and some washers require orientation. Due to their relatively low head to outer diameter ratio and short length, headed Compression Limiters and washers are more difficult to mechanically orient than bolts. Conversely, symmetrical Compression Limiters do not need to be oriented. An assembly with a flanged bolt only requires one component’s orientation while that with a headed Compression Limiter or washer requires two components be oriented.

There are several methods to ensure sufficient bearing surface under the bolt’s head. These include the use of a flanged bolt, washer or headed Compression Limiter.
The individual component cost, ease or complexity of assembly and overall cost of each configuration influence which method is best suited for each application.
How much plastic should be compressed?
Ideally, Compression Limiter length is equal to or slightly less than the host thickness. The amount of material compressed under the bolt’s head varies depending on the application’s loading and plastic properties. This area of compression must be large enough to withstand forces attempting to pull the assembly apart, yet small enough to allow sufficient plastic compression so that the Compression Limiter contacts both the bolt and the mating component.
Design intangibles
Use of a headed Compression Limiter or flanged bolt in serviceable assemblies may be preferable as there would be no washer that could be accidentally omitted during reassembly. These are also preferable in applications where there are multiple assembly locations and poor quality control.
Individual component costs
Generally, fasteners are the least expensive components in an assembly. The following chart shows representative pricing for each component combination previously discussed based on an annual usage of 1 million assemblies incorporating an M6 joint.

Relative cost differences between bolts and Compression Limiters vary depending on component supplier and bolt characteristics.
Relative cost differences between bolts and Compression Limiters vary depending on component supplier and bolt characteristics. Of these three potential combinations, the method with a washer, bolt and non-headed Compression Limiter provides the lowest component cost for controlling bearing surface. However, as previously stated, the cost of the fastening components is often the least significant compared to the overall cost of the assembly.

The following shows an estimate overall cost analysis of each configuration assuming a $50 USD/hour labor cost to assemble 1 million components
Overall cost
The following shows an estimate overall cost analysis of each configuration assuming a $50 USD per hour labor cost to assemble 1 million components.
Conclusion
The best method to ensure adequate bearing surface on the plastic in a bolted assembly depends on an application’s requirements and limitations. A washer may be preferred in lower volume and non-serviced applications. In higher volume, automated and serviceable applications, a non-headed Compression Limiter with a flanged bolt is the easiest to assemble and provides the lowest total cost. Both configurations with a washer or flanged bolt will provide a lower cost solution than using a headed Compression Limiter.
Although this article offers general design guidelines, it is recommended that application engineers who specialize in fastening and joining be consulted to ensure a properly configured joint is employed for each application.
Spirol
www.spirol.com



![A photo of the Medtronic GI Genius ColonPro polyp detection system flagging a potential sign of colon cancer during a colonoscopy. [Photo courtesy of Medtronic]](https://www.medicaldesignandoutsourcing.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/Medtronic-GI-Genius-doctors-268x170.jpg)
