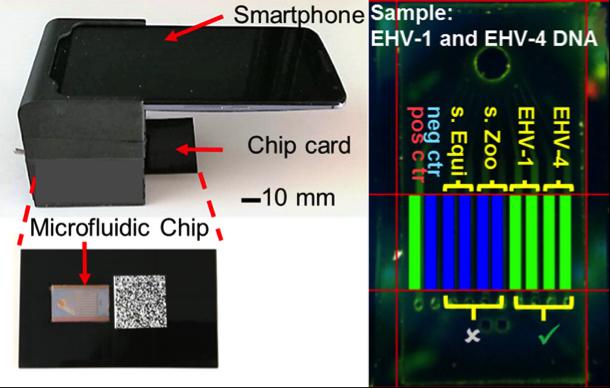
The system uses a commercial smartphone to acquire and interpret real-time images of an enzymatic amplification reaction that takes place in a silicon microfluidic chip that generates green fluorescence and displays a visual read-out of the test. The system is composed of an unmodified smartphone and a portable 3-D-printed cradle that supports the optical and electrical components, and interfaces with the rear-facing camera of the smartphone. (Credit: Micro & Nanotechnology Laboratory, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign)
A multidisciplinary group that includes the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaignand the University of Washington at Tacoma has developed a novel platform to diagnose infectious disease at the point-of-care, using a smartphone as the detection instrument in conjunction with a test kit in the format of a credit card. The group is led by Illinois Electrical and Computer EngineeringProfessor Brian T. Cunningham; Illinois Bioengineering Professor Rashid Bashir; and, University of Washington at Tacoma Professor David L. Hirschberg, who is affiliated with Sciences and Mathematics, division of the School of Interdisciplinary Arts and Sciences.
Findings have been published in Analytical Chemistry, demonstrating detection of four horse respiratory diseases, and in Biomedical Microdevices, where the system was used to detect and quantify the presence of Zika, Dengue, and Chikungunya virus in a droplet of whole blood. Project collaborators include Dr. David Nash, a private practice equine expert and veterinarian in Kentucky, and Dr. Ian Brooks, a computer scientist at the National Center for Supercomputing Applications.
The low-cost, portable, smartphone-integrated system provides a promising solution to address the challenges of infectious disease diagnostics, especially in resource-limited settings or in situations where a result is needed immediately. The diagnostic tool’s integration with mobile communications technology allows personalized patient care and facilitates information management for both healthcare providers and epidemiological surveillance efforts. Importantly, the system achieves detection limits comparable to those obtained by laboratory-based methods and instruments, in about 30 minutes.
A useful capability for human point-of-care (POC) diagnosis or for a mobile veterinary laboratory, is to simultaneously test for the presence of more than one pathogen with a single test protocol, which lowers cost, saves time and effort, and allows for a panel of pathogens, which may cause similar symptoms, to be identified.
Infectious diseases remain the world’s top contributors to human death and disability, and with recent outbreaks of Zika virus infections, there is a keen need for simple, sensitive, and easily translatable point-of-care tests. Zika virus appeared in the international spotlight in late 2015 as evidence emerged of a possible link between an epidemic affecting Brazil and increased rates of microcephaly in newborns. Zika has become a widespread global problem–the World Health Organization (WHO) documented last year that since June 2016, 60 nations and territories report ongoing mosquito-borne transmission. Additionally, since Zika virus infection shares symptoms with other diseases such as Dengue and Chikungunya, quick, accurate diagnosis is required to differentiate these infections and to determine the need for aggressive treatment or quarantine.
For the research effort, horses were used as an animal model for respiratory disease in man and food animals. Says Dr. David Nash “You can often more easily develop diagnostic tools for human use by coming in to development from the animal side of things first. Many diseases show up first in animals, kind of the canary in the coal mine.”
A key project contributor, Dr. Nash comments on the financial impact of infectious disease outbreaks in horses: “It’s costly to horse owners and trainers, and disrupts the business operations of all equine sports. Consider this–on December 25, 2016 a single horse stabled at the Fair Grounds Race Course in New Orleans experienced a fever and subsequently developed neurological symptoms. The state diagnostic lab was 100 miles away and was closed for the Christmas holiday. The end result was an equine herpesvirus-1 (EHV-1) outbreak that resulted in the quarantine of over 200 horses at the racetrack and a serious financial loss for horse owners and the racetrack owner, Churchill Downs, Inc. Imagine the consequences if they ever had to postpone the Kentucky Derby due to a disease outbreak.”
The technology is intended to enable clinicians to rapidly diagnose disease in their office or in the field, resulting in earlier, more informed patient management decisions, while markedly improving the control of disease outbreaks. An important prerequisite for the widespread adoption of point-of-care tests at the patient’s side is the availability of detection instruments that are inexpensive, portable, and able to share data wirelessly over the Internet.
The system uses a commercial smartphone to acquire and interpret real-time images of an enzymatic amplification reaction that takes place in a silicon microfluidic chip that generates green fluorescence and displays a visual read-out of the test. The system is composed of an unmodified smartphone and a portable 3D-printed cradle that supports the optical and electrical components, and interfaces with the rear-facing camera of the smartphone.
The software application operating on the smartphone gathers information about the tests conducted on the microfluidic card, patient-specific information, and the results from the assays, that are then communicated to a cloud storage database.
Dr. Nash observes that, “This project is a game changer. This is the future of medicine–empowered front-line healthcare professionals. We can’t stop viruses and bacteria, but we can diagnose more quickly. We were able to demonstrate the clear benefit to humankind, as well as to animals, during the proposal phase of the project, and our results have proved our premise. Next, I want to go into the field, multiple sites, multiple geographic locations, and test in real-world situations.”
U of I graduate student and research assistant Fu Sun sees this project as fulfillment of one of her primary career objectives: “I entered graduate school with the hope to make a better world by developing biomedical devices that can facilitate effective disease prevention, diagnosis, or treatment. This project is in line with my goal since it provides a point-of-care solution for the fast diagnosis of infectious diseases. Connected to a cloud database through a smartphone, it helps healthcare providers in the field embrace the era of big data and the Internet of Things.”
The system represents the only platform to date that can multiplex detection of viral and other nucleic acid targets on a portable point-of-care setup using one droplet of bodily fluid, including whole blood.
For Dr. Nash the experience of working with the University of Illinois team and other project collaborators was a great one, as he remarks “A diverse team was actually created here. A wicked smart group of people! I can’t envision going into a project without engineers now.”




