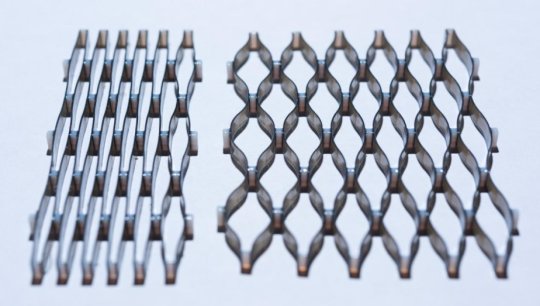
A lattice created by a multi-material 3D printer at Georgia Institute of Technology that can permanently expand to eight times its original width after exposure to heat. (Credit: Rob Felt)
A team of researchers from Georgia Institute of Technology and two other institutions has developed a new 3D printing method to create objects that can permanently transform into a range of different shapes in response to heat.
The team, which included researchers from the Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) and Xi’an Jiaotong University in China, created the objects by printing layers of shape memory polymers with each layer designed to respond differently when exposed to heat.
“This new approach significantly simplifies and increases the potential of 4D printing by incorporating the mechanical programming post-processing step directly into the 3D printing process,” says Jerry Qi, a professor in the George W. Woodruff School of Mechanical Engineering at Georgia Tech. “This allows high-resolution 3D printed components to be designed by computer simulation, 3D printed, and then directly and rapidly transformed into new permanent configurations by simply heating.”
The research was reported April 12 in the journal Science Advances, a publication of the American Association for the Advancement of Science. The work is funded by the U.S. Air Force Office of Scientific Research, the U.S. National Science Foundation and the Singapore National Research Foundation through the SUTD DManD Centre.
Their development of the new 3-D printed objects follows earlier work the team had done using smart shape memory polymers (SMPs), which have the ability to remember one shape and change to another programmed shape when uniform heat is applied, to make objects that could fold themselves along hinges.
“The approach can achieve printing time and material savings up to 90 percent, while completely eliminating time-consuming mechanical programming from the design and manufacturing workflow,” Qi says.
To demonstrate the capabilities of the new process, the team fabricated several objects that could bend or expand quickly when immersed in hot water — including a model of a flower whose petals bend like a real daisy responding to sunlight and a lattice-shaped object that could expand by nearly eight times its original size.
“Our composite materials at room temperature have one material that is soft but can be programmed to contain internal stress, while the other material is stiff,” says Zhen Ding, a postdoc researcher at Singapore University of Technology and Design. “We use computational simulations to design composite components where the stiff material has a shape and size that prevents the release of the programmed internal stress from the soft material after 3D printing. Upon heating the stiff material softens and allows the soft material to release its stress and this results in a change — often dramatic — in the product shape.”
The new 4D objects could enable a range of new product features, such as allowing products that could be stacked flat or rolled for shipping and then expanded once in use, the researchers says. Eventually, the technology could enable components that could respond to stimuli such as temperature, moisture or light in a way that is precisely timed to create space structures, deployable medical devices, robots, toys and range of other structures.
“The key advance of this work is a 4-D printing method that is dramatically simplified and allows the creation of high-resolution complex 3D reprogrammable products,” says Martin L. Dunn a professor at Singapore University of Technology and Design who is also the director of the SUTD Digital Manufacturing and Design Centre. “It promises to enable myriad applications across biomedical devices, 3D electronics, and consumer products. It even opens the door to a new paradigm in product design, where components are designed from the onset to inhabit multiple configurations during service.”


