Researchers have witnessed – for the first time – cancer cells being targeted and destroyed from the inside, by an organo-metal compound discovered by the University of Warwick.
Professor Peter J. Sadler, and his group in the Department of Chemistry, have demonstrated that Organo-Osmium FY26 – which was first discovered at Warwick – kills cancer cells by locating and attacking their weakest part.
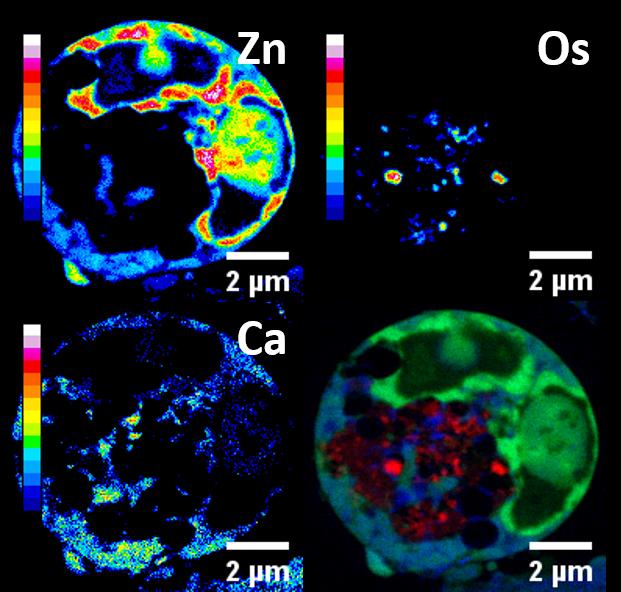
Ovarian cancer cells under nano-focus (2 micron scale), are showing FY26, zinc and calcium. (Credit: University of Warwick)
This is the first time that an Osmium-based compound – which is fifty times more active than the current cancer drug cisplatin – has been seen to target the disease.
Using the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF), researchers analysed the effects of Organo-Osmium FY26 in ovarian cancer cells – detecting emissions of X-ray fluorescent light to track the activity of the compound inside the cells.
Looking at sections of cancer cells under nano-focus, it was possible to see an unprecedented level of minute detail. Organelles like mitochondria, which are the ‘powerhouses’ of cells and generate their energy, were detectable.
In cancer cells, there are errors and mutations in the DNA of mitochondria, making them very weak and susceptible to attack.
FY26 was found to have positioned itself in the mitochondria – attacking and destroying the vital functions of cancer cells from within, at their weakest point.
Researchers were also able to see natural metals which are produced by the body – such as zinc and calcium – moving around the cells. Calcium in particular is known to affect the function of cells, and it is thought that this naturally-produced metal helps FY26 to achieve an optimal position for attacking cancer.
More than half of all cancer chemotherapy treatments currently use platinum compounds, which were introduced nearly 40 years ago, so there is a need to explore the benefits which other precious metals could bring.
Although this research was conducted on ovarian cancer cells, the ground-breaking results are applicable to a wider range of cancers.
FY26 has been shown to be more selective between normal cells and cancer cells than cisplatin – having a greater effect on cancer cells than on healthy ones.
Professor Sadler comments that this research could lead to new cancer treatments:
“Cancer drugs with new mechanisms of actions which can combat resistance and have fewer side-effects are urgently needed.
“The advanced nano-focussed x-ray beam at ESRF has not only allowed us to locate the site of action of our novel Organo-Osmium FY26 candidate drug in cancer cells at unprecedented resolution, but also study the movement of natural metals such as zinc and calcium in cells. Such studies open up totally new approaches to drug discovery and treatment”
Professor Sadler’s group, including research fellows Dr. Carlos Sanchez and Dr Isolda Romero Canelon, gained their results with Dr. Peter Cloetens and colleagues at the ESRF in Grenoble, France – a powerful synchrotron source which emits extremely powerful X-ray beams.
Dr. Peter Cloetens comments on the process:
“These kinds of experiments are normally performed using bigger doses than what would be done in real life or on a coarse scale that does not provide a clear picture of the processes that take place. On the new nano-imaging ID16A beamline, however, by combining a very tight focus and high flux, we could get a real picture of where the drug goes in a single cell using real-life pharmacological doses.”


