Tests that can distinguish whether HIV-positive people are infected with a drug-resistant strain or a non-resistant strain allow patients to get the most effective treatment as quickly as possible. In the November edition of the Journal of Molecular Diagnostics, a team of Brown University researchers describes a new method that works faster and more sensitively in lab testing than the current standard technologies.
The main advance enabling that improved performance is that the system operates directly on the virus’ more readily available RNA rather than requiring extra, potentially error-prone steps to examine DNA derived from RNA. In a single tube, the system can first combine two engineered probes (ligation) if a mutation is present and then make many copies of those combined probes (amplification) for detection.
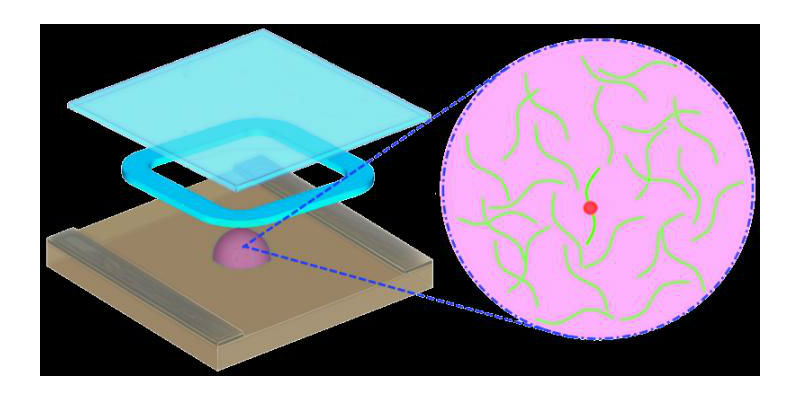
A Brown team has developed a new method for analyzing the the RNA (green strands) of HIV for mutations (red dot) that convey drug resistance. The system does not require transcription of RNA to DNA, as current technologies do, and works within one solution (purple droplet). (Credit: Lei Zhang/Brown University)
“LRA (ligation on RNA amplification) uniquely optimizes two enzymatic reactions — RNA-based ligation, and quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification — into a single system,” said Anubhav Tripathi, professor of engineering at Brown and corresponding author on the paper. “Each HIV contains about 10,000 nucleotides, or building blocks, in its genetic material, and a drop of blood from a patient with resistant HIV can contain thousands to millions of copies of HIV. To find that one virus, out of thousands to millions, which is mutated at just a single nucleotide is like finding a needle in a haystack.”
The experiments reported in the paper show that the LRA test was sensitive enough to find a commonly sought K103N mutation in concentrations as low as one mutant per 10,000 strands of “normal” viral RNA. The LRA detection worked within two hours, while alternative technologies such as ASPCR or pyrosequencing, can take as long as eight.
LRA works by sending in many copies of a pair of short engineered probes of genetic material to complement the RNA in the HIV sample. Under optimized conditions, those pairs that perfectly match the target HIV RNA containing a mutation that causes drug resistance can rapidly become fused together, or ligated, by an enzyme. If there is a single nucleotide difference, the pair won’t fuse.
The fusing of the engineered genetic probes is designed to happen at room temperature. After a short period, the LRA system then heats the slightly alkaline solution, which shuts off the fusing reaction but turns on the amplification (copying) of fused pairs. That allows the LRA system to produce a strong signal of fused pairs, if there are any. All this happens in a single step, without any need to change solution.
Aiming for the Clinic
The development of LRA is the product of a collaboration led by Tripathi and Dr. Rami Kantor, associate professor of medicine in the Warren Alpert Medical School. Kantor, who is also an HIV specialist at The Miriam Hospital and co-senior author of the paper, works in developing nations such as Kenya and India, monitoring HIV resistance. One day when Tripathi was at the Lifespan/Tufts/Brown Center for AIDS Research Retrovirology Core Laboratory to discuss his work, Kantor suggested a collaboration with the end goal of developing a cheap, quick and accurate HIV drug resistance mutation detection system for use in developing nations.
“We met soon thereafter and started working together on various developments and implementations of the ideas and on the integration of our worlds,” Kantor said.
The authors acknowledge in the paper that what they demonstrate, while successful in the lab, is clearly not ready for deployment in the field. The lab tests, for example, are shown to work on HIV RNA derived from plasmids, laboratory viral strains, not on samples from circulating viruses found in ailing patients. The RNA fragments were prepared in Kantor’s lab by Dr. Mia Coetzer, assistant professor of medicine and a co-author on the paper.
“The next steps are to continue the development of LRA and other methods on patient samples to detect additional mutations and address specific HIV challenges related to mutation detection, such as enormous genomic diversity,” Kantor said, “and work on incorporation of such methods onto a point-of-care device that would satisfy the infrastructure and low-cost needs of resource limited settings.”




