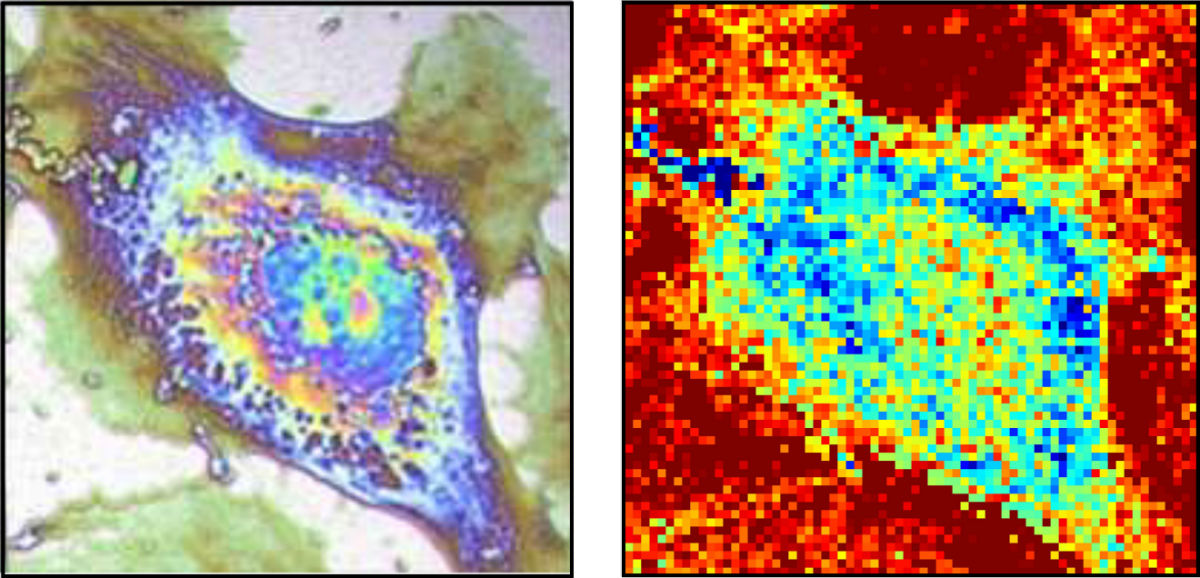
On the left, a classical phase contrast image of a cell obtained via a standard microscope. On the right, a thermal image of the same cell recorded with the team’s thermal imaging device. (Credit: Bordeaux University)
Researchers in France working wondered whether it might be possible to tap into active thermography camera technology — behind night-vision equipment and the thermal imaging of buildings — to create a sort of thermal microscope to produce heat maps of single cells to help them understand the thermal behavior of the cells or go a step even further by detecting diseased conditions at the sub-cell scale. They report their work in Applied Physics Letters.
Thermal properties of cells regulate their ability to store, transport or exchange heat with their environment. So gaining control of these properties is of great interest for optimizing cryopreservation — the process of freezing and storing blood or tissues, which is also used when transporting organs for transplants.
Cell activity influences thermal properties, and at the tissue level this explains why infected wounds feel warm to the touch. Cancer cells, in particular, contain a thermal signature that reflects a higher metabolism than those of healthy cells. This feature is useful for grading tumors and can be used to complement classical histological analysis.
A team of researchers in France working within this realm wondered whether it might be possible to tap into active thermography camera technology — behind night-vision equipment and the thermal imaging of buildings — to create a sort of thermal microscope to produce heat maps of single cells to help them understand the thermal behavior of the cells or go a step even further by detecting diseased conditions at the sub-cell scale.
As the team led by the University of Bordeaux reports in the journal Applied Physics Letters, from AIP Publishing, the first step of their work involved growing cells atop a nanometric titanium sheet. Titanium was selected because it’s the main constituent of bone implants.
“We flash heat the titanium sheet by only a few degrees with a micrometric laser spot,” explained Thomas Dehoux, a researcher at CNRS, the French National Centre for Scientific Research. “You might say we ‘heat the spot’ to image the temperature variations on the bottom side of the sheet. If there is no cell on the other side, the heat remains in the titanium sheet and the temperature increases.” Conversely, if there is a cell on the other side it will absorb heat and create a cold spot on the sheet.
The temperature variations involved are quite small and occur on a tiny micron-sized spot — a hundredth of a human hair — so the researchers can’t rely on a standard thermometer. Instead, they measure the titanium sheet’s “bulging” upon heating.
What exactly do they look for? “When the temperature is high — without a cell on the other side — the metal sheet dilates locally and creates a bump,” said Dehoux. “When the temperature decreases — a cell is probed — the sheet’s profile returns to normal. We’re able to detect this effect with a second laser beam that’s deflected by the movement of the bottom surface, which gives us unprecedented sensitivity.”
Each part of the cell absorbs heat differently, thanks to the inhomogeneities in its thermal properties. “This allows us to see through the metal sheet and produce a thermal image of the cell,” he added.
While many existing modalities exploit differences in optical properties to image cells, most use fluorescent marking to increase contrast. Such images reveal the structure and molecular composition of the cell, but provide no useful details about its thermal properties.
The significance of the team’s model is that it provides an image of a single cell with micrometer resolution via a contrast based on the cell’s thermal properties. “Before now, no such image has ever been produced — it’s like looking at cells with night-vision goggles,” pointed out Dehoux.
In terms of applications, the team hopes their technique can serve as a new tool to perform histological analysis and detect diseased cells within samples of patients’ tissue. “It might also reveal new information about the behavior of cells because we will be able to observe them with a new contrast,” said Dehoux.
What’s next for the team? Since this is the first time images of this nature have been produced, the technique could use a bit more optimization. “In particular, we want to improve its acquisition time and sensitivity to enable observation of cells in real time,” Dehoux noted. “We’d also like to test the effect of anti-cancer drugs on the thermal properties of cells to see if new thermal strategies can be defined to stop cancer.”




