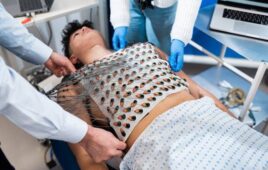
 Caltech researchers are touting an “electronic skin” (e-skin) applied to real skin that can monitor health indicators with fuel from the body’s own waste products instead of batteries.
Caltech researchers are touting an “electronic skin” (e-skin) applied to real skin that can monitor health indicators with fuel from the body’s own waste products instead of batteries.
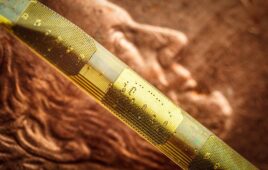
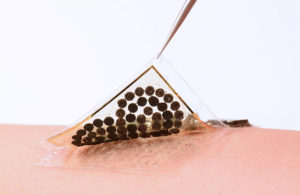
The e-skin, made from soft, flexible rubber, can be embedded with sensors for monitoring heart rate, body temperature, blood sugar levels and metabolic byproducts that are health indicators. Researchers published a paper describing the e-skin titled “Biofuel-powered soft electronic skin for multiplexed and wireless sensing” in the journal Science Robotics.
Instead of a battery, the e-skin runs on biofuel cells powered by human sweat, according to Caltech engineering professor Wei Gao.
“One of the major challenges with these kinds of wearable devices is on the power side,” Gao said in a news release. “Many people are using batteries, but that’s not very sustainable. Some people have tried using solar cells or harvesting the power of human motion, but we wanted to know, ‘Can we get sufficient energy from sweat to power the wearables?’ and the answer is yes.”
Human sweat contains high levels of chemical lactate that the fuel cells in the e-skin absorb to combine with oxygen from the atmosphere, generating water and pyruvate. During operation, the cells generate enough electricity to power sensors and a Bluetooth device to allow for the e-skin to wirelessly transmit readings from its sensors.
Gao noted that the e-skin also needs to last a long time with high-power intensity and minimal degradation. The biofuel cells are made from carbon nanotubes with a platinum/cobalt catalyst and composite mesh holding an enzyme to break down lactate, allowing the cells to generate continuous, stable power output over multiple days. Gao also plans to develop a variety of sensors so the e-skin can be used for multiple purposes.
“We want this system to be a platform,” Gao said. “In addition to being a wearable biosensor, this can be a human-machine interface. The vital signs and molecular information collected using this platform could be used to design and optimize next-generation prosthetics. “