Connectivity is at the core of the devices transforming healthcare, yet interconnects are often an afterthought. Selecting the right connectors in the initial design process supports better overall performance and functionality.
Medtech designers face some of the toughest design challenges in the electronics industry. Portable medical devices must be compact and lightweight enough to be moved easily, while tolerating the vibration, shock, and impact of frequent transport. Because these products operate within a larger network of connected devices and systems, electromagnetic interference (EMI) and interoperability should also be considered early on in the design process.
In addition to the usual design considerations like size, torque, pin count, and locking mechanism, connectors used in medical devices must withstand moisture, dust, chemicals, and high temperatures. They must be easy to use and durable enough to last thousands of mating cycles, all while meeting the industry’s stringent regulations.
Maximizing wireless connectivity

MHF® micro RF coaxial connectors connect antennas to radios while maximizing performance in minimal space. [Image courtesy of I-PEX]
Bluetooth is widely deployed in healthcare applications due to its ease of use and low power consumption. Drawbacks include low-speed data transmission at limited range. New Wi-Fi 6/6E technologies offer stable, higher-speed, large-capacity communication. However, Wi-Fi in general struggles to maintain stable connections while devices move between indoor and outdoor locations.
Cellular networks offer more widespread coverage, reliability, and seamless interoperability with existing IT infrastructure. Disadvantages include cost, higher power consumption, and security concerns. Maximizing device connectivity is a combination of choosing the right electronic components, including interconnects, and the most suitable wireless technology for the application’s requirements.
The need for high-speed, high-quality data transmission
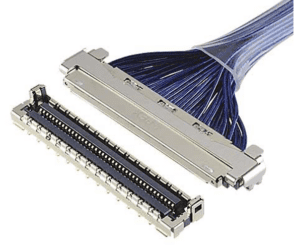
Vertical-mating CABLINE®-UM micro-coaxial connector with ZenShield®. [Image courtesy of I-PEX]
Here’s how interconnects apply to portable ultrasound probe assemblies

Portable ultrasound probe assembly [Image: Adobe Stock]
These systems typically use fine-gauge micro-coaxial cable ranging from 36-42 AWG to reduce equipment weight and size, and support cable flexibility. The impedance-controlled micro-coaxial wires and EMI-shielded connectors transmit signals to and from the transducer on the ultrasound probe. Their signal lines are shielded to prevent EMI and crosstalk. This enables the highest signal quality of the probe data to the signal processors to ensure the transmission of clean images.
Connector solutions include direct termination of the cable to paddle cards and board-to-board connectors, or direct termination to other connector types. Paddle cards are small PCBs designed for direct wire termination, but often have a board-to-board connector on the other side of the card, allowing the paddle card to make the connection between the wires and the connector.
Other connector types can terminate the wires directly, without the PCB paddle card. Many micro-coaxial cable connectors, for instance, have a modular construction that not only supports direct termination, but also allows the probe assemblies to be made in pieces and then assembled, which can positively impact production efficiency, especially in the case of repairs and rework.

MINIDOCK I/OTM connectors with low-insertion-force cable plug terminations support up to 5,000 mating cycles. [Image courtesy of I-PEX]
How I-PEX helps OEMs successfully build portable medical devices
I-PEX offers some of the world’s most advanced, high-quality, high-speed, very small connectors. Their ultra-precision manufacturing process has been perfected over the past 60 years, and their connectors have a proven track record in medical device applications. To learn more about I-PEX’s interconnect solutions, visit www.l-PEX.com.