Physicists at The University of Texas at Arlington have shown that using microwaves to activate photosensitive nanoparticles produces tissue-heating effects that ultimately lead to cell death within solid tumors.
“Our new method using microwaves can propagate through all types of tissues and target deeply situated tumors,” said Wei Chen, UTA professor of physics and lead author of the study published this month in he Journal of Biomedical Nanotechnologytitled “A new modality of cancer treatment-nanoparticle mediated microwave induced photodynamic therapy.”
Photodynamic therapy kills cancer cells when a nanoparticle introduced into tumor tissue generates toxic singlet oxygen after being exposed to light. Singlet oxygen is a highly reactive type of oxygen that irreversibly damages cell mitochondria and eventually causes cell death.
“Up to now, photodynamic therapy, which depends on visible, ultraviolet or near infrared light, was considered effective for skin cancers or cancers close to the skin surface,” Chen said. “Our new concept combining microwaves with photodynamic therapy opens up new avenues for targeting deeper tumors and has already proven effective in rapidly and safely reducing tumor size.”
In prior studies, the researchers had identified a new type of nanoparticle, copper-cysteamine or Cu-Cy, that could be activated by X-rays to produce singlet oxygen and slow the growth of tumors. X-ray radiation, however, poses significant risks to patients and can harm healthy tissue.
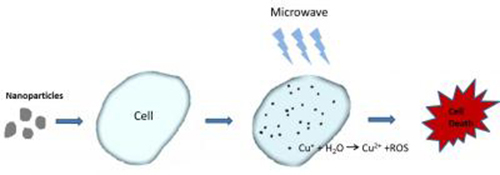
Photo explaining the method. (Credit: UTA)
In this new lab study, the team demonstrated that the nanoparticle Cu-Cy also can be activated by microwaves, which can be targeted directly at the tumor itself without harming surrounding tissue.
“Our new microwave-induced photodynamic therapy offers numerous advantages, the most significant of which is increased safety,” Chen said. “Our nanoparticle Cu-Cy also demonstrates very low toxicity, is easy to make and inexpensive, and also emits intense luminescence, which means it can also be used as an imaging agent.”
The researchers demonstrated that both in vitro and in vivo studies on an osteosarcoma cell line showed significant cell destruction using copper cysteamine nanoparticles under microwave activation. The heating effects and the release of copper ions from copper cysteamine upon activation was the main mechanism for the generation of the reactive oxygen needed for cancer cell destruction.
Chen was joined on this research by Lun Ma, a UTA research assistant professor in physics, as well as Mengyu Yao, Lihua Li and Yu Zhang from the Guangdong Key Laboratory of Orthopaedic Technology and Implant Materials in Guangzhou, China, and Junying Zhang from the Physics Department at Beihang University in Beijing, China. The U.S. Army Medical Research Acquisition Activity, the National Science Foundation and Department of Homeland Security’s joint Academic Research Initiative program, the National Basic Research Program of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the five-year plan of the Chinese Military, all supported this research.
“This new invention is largely based on the new photosensitizer copper cysteamine that we invented and patented, and I would like to thank all our team members, particularly Dr. Lun Ma, for the time and energy spent on this project,” Chen said.
Alex Weiss, UTA chair of the Physics Department, emphasized the importance of this research in the context of UTA’s increasing focus on health and the human condition within the Strategic Plan 2020: Bold Solutions|Global Impact.
“Dr. Chen’s research into nanoparticle activation has led to important discoveries that could potentially transform cancer treatment,” Weiss said. “This new paper on the possibilities of microwave activation demonstrates yet again how Dr. Chen’s search for new modalities of therapy could play a key role in finding safe, viable and inexpensive treatments for cancer.”
