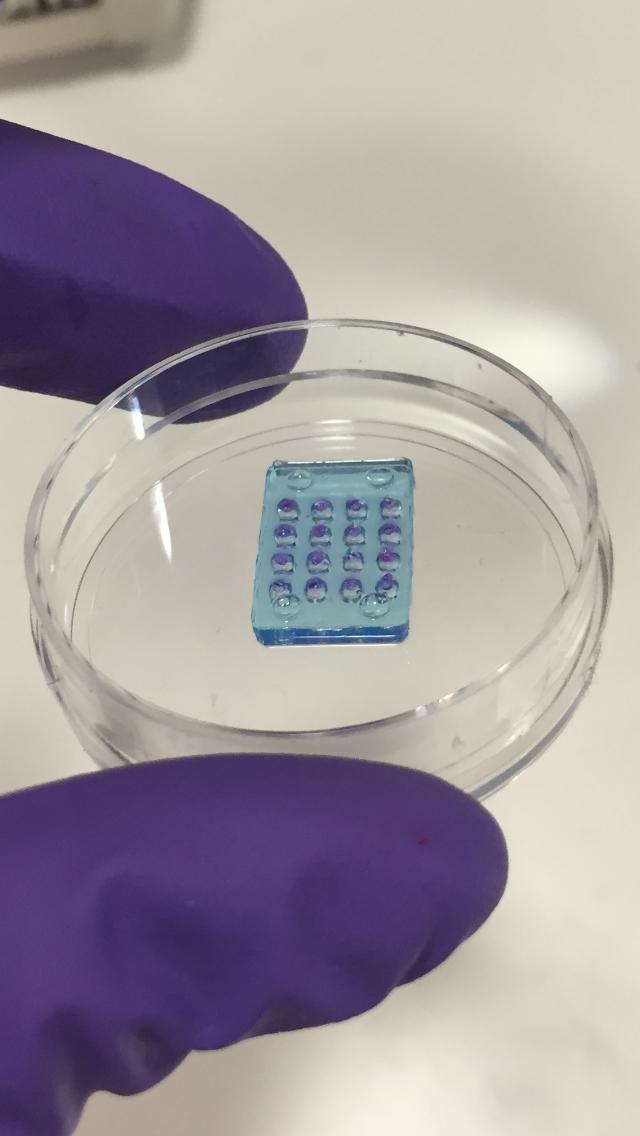
The retina replica consists of soft water droplets (hydrogels) and biological cell membrane proteins. Designed like a camera, the cells act as pixels, detecting and reacting to light to create a grey scale image. (Credit: Oxford University)
A synthetic, soft tissue retina developed by an Oxford University student could offer fresh hope to visually impaired people.
Until now, all artificial retinal research has used only rigid, hard materials. The new research, by Vanessa Restrepo-Schild, a 24-year-old Dphil student and researcher at the Oxford University, Department of Chemistry, is the first to successfully use biological, synthetic tissues, developed in a laboratory environment. The study could revolutionise the bionic implant industry and the development of new, less invasive technologies that more closely resemble human body tissues, helping to treat degenerative eye conditions such as retinitis pigmentosa.
Just as photography depends on camera pixels reacting to light, vision relies on the retina performing the same function. The retina sits at the back of the human eye, and contains protein cells that convert light into electrical signals that travel through the nervous system, triggering a response from the brain, ultimately building a picture of the scene being viewed.
Vanessa Restrepo-Schild led the team in the development of a new synthetic, double layered retina which closely mimics the natural human retinal process. The retina replica consists of soft water droplets (hydrogels) and biological cell membrane proteins. Designed like a camera, the cells act as pixels, detecting and reacting to light to create a grey scale image. The Colombian native says, “The synthetic material can generate electrical signals, which stimulate the neurons at the back of our eye just like the original retina.”
The study, published in the journal Scientific Reports, shows that unlike existing artificial retinal implants, the cell-cultures are created from natural, biodegradable materials and do not contain foreign bodies or living entities. In this way the implant is less invasive than a mechanical devise, and is less likely to have an adverse reaction on the body. Miss Restrepo-Schild added: ‘The human eye is incredibly sensitive, which is why foreign bodies like metal retinal implants can be so damaging, leading to inflammation and/or scaring. But a biological synthetic implant is soft and water based, so much more friendly to the eye environment.’
Of the motivation behind the ground-breaking study, Miss Restrepo-Schild says, “I have always been fascinated by the human body, and want to prove that current technology could be used to replicate the function of human tissues, without having to actually use living cells. I have taken the principals behind vital bodily functions, e.g. our sense of hearing, touch and the ability to detect light, and replicated them in a laboratory environment with natural, synthetic components. I hope my research is the first step in a journey towards building technology that is soft and biodegradable instead of hard and wasteful.”
Although at present the synthetic retina has only been tested in laboratory conditions, Miss Restrepo-Schild is keen to build on her initial work and explore potential uses with living tissues. This next step is vital in demonstrating how the material performs as a bionic implant.
Miss Restrepo-Schild has filed a patent for the technology and the next phase of the work will see the Oxford team expand the replica’s function to include recognising different colours. Working with a much larger replica, the team will test the material’s ability to recognise different colours and potentially even shapes and symbols. Looking further ahead the research will expand to include animal testing and then a series of clinical trials in humans.




