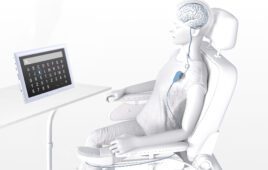
Scientists have developed sensor technology for a robotic prosthetic arm that detects signals from nerves in the spinal cord.
To control the prosthetic, the patient has to think like they are controlling a phantom arm and imagine some simple maneuvers, such as pinching two fingers together. The sensor technology interprets the electrical signals sent from spinal motor neurons and uses them as commands.
A motor neuron is a nerve cell that is located in the spinal cord. Its fibres, called axons, project outside the spinal cord to directly control muscles in the body.
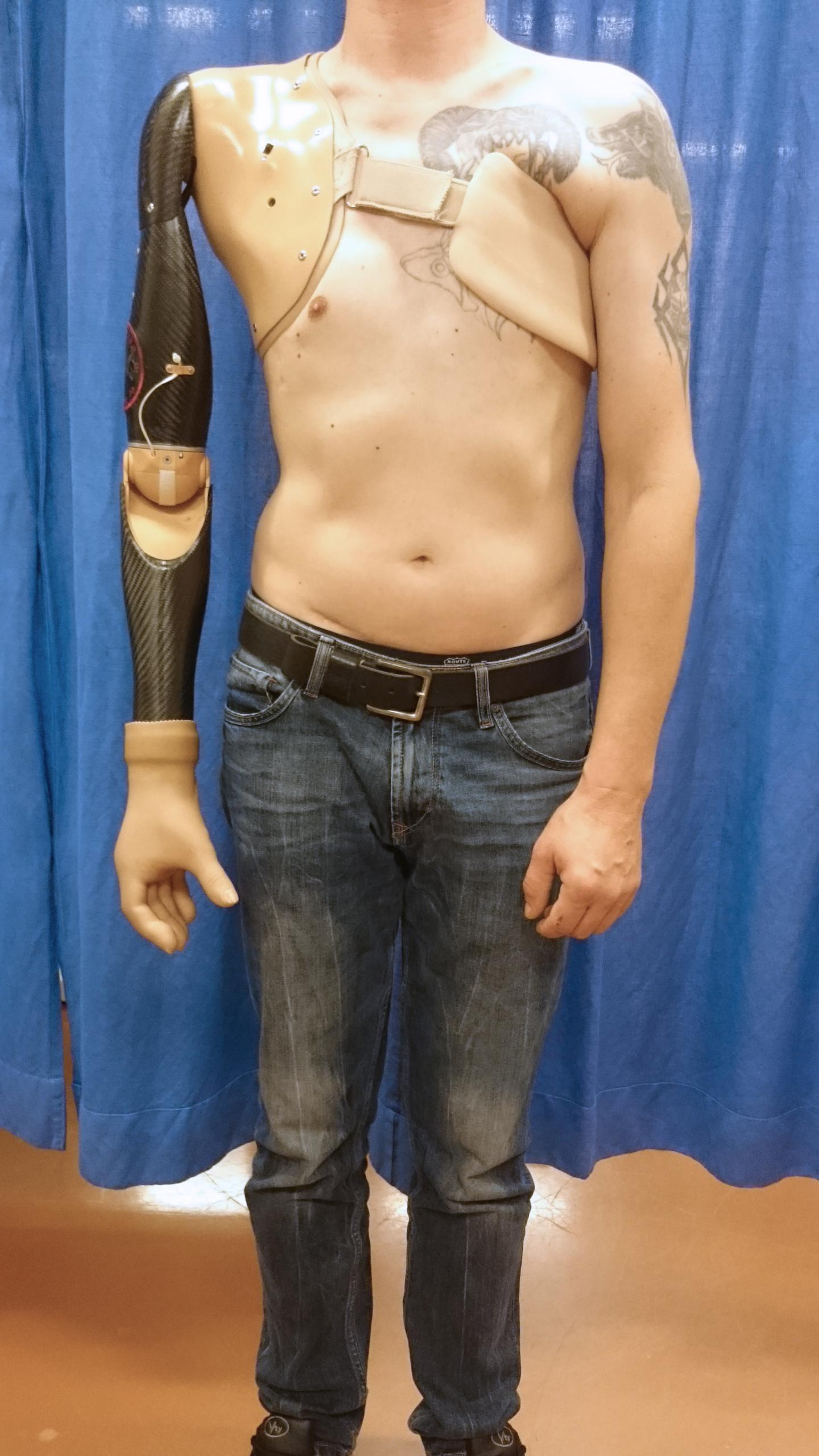
This is an image of the sensor system and robotic prosthetic operated by a patient who took part in the laboratory experiments as part of the study. (Credit: Imperial College London)
Robotic arm prosthetics currently on the market are controlled by the user twitching the remnant muscles in their shoulder or arm, which are often damaged. This technology is fairly basic in its functionality, only performing one or two grasping commands. This drawback means that globally around 40 to 50 percent of users discard this type of robotic prosthetic.
The team in today’s study, published in the journal Nature Biomedical Engineering, say detecting signals from spinal motor neurons in parts of the body undamaged by amputation, instead of remnant muscle fibre, means that more signals can be detected by the sensors connected to the prosthetic. This means that ultimately more commands could be programmed into the robotic prosthetic, making it more functional.
Dr. Dario Farina, who is now based at Imperial College London, carried out much of the research while at the University Medical Centre Gottingen. The research was conducted in conjunction with Dr. Farina’s co-authors in Europe, Canada and the USA.
Dr. Farina, from the Department of Bioengineering at Imperial says, “When an arm is amputated the nerve fibres and muscles are also severed, which means that it is very difficult to get meaningful signals from them to operate a prosthetic. We’ve tried a new approach, moving the focus from muscles to the nervous system. This means that our technology can detect and decode signals more clearly, opening up the possibility of robotic prosthetics that could be far more intuitive and useful for patients. It is a very exciting time to be in this field of research.”
The researchers carried out lab-based experiments with six volunteers who were either amputees from the shoulder down or just above the elbow. After some physiotherapy training, the amputees were able to make a more extensive range of movements than would be possible using a classic muscle-controlled robotic prosthetic. They came to this conclusion by comparing their research to previous studies on muscle-controlled robotic prosthetics.
The volunteers were able to move the elbow joint and do radial movements – moving the wrist from side to side – as well as opening and closing the hand. This means that the user has all basic hand and arm functions of a real arm.
Further refinements are needed to make the technology more robust, but the researchers suggest the current model could be on the market in the next three years.
To take part in the study, volunteers underwent a surgical procedure at the Medical University of Vienna that involved re-routing parts of their Peripheral Nervous System (PNS), connected with hand and arm movements, to healthy muscles in their body. Depending on the type of amputation, this re-routing was either directed to the pectoral muscle in the chest or the bicep in the arm.
This enabled the team to clearly detect the electrical signals sent from the spinal motor neurons – a process the team liken to amplification of the signals.
To create the technology, the researchers decoded and mapped some of the information in electrical signals sent from the re-routed nerve cells and then interpreted them in computer models. These models were then compared to models of healthy patients, which helped them to corroborate the results. Ultimately, the scientists want to decode the meaning behind all signals sent from these motor neurons, so that they can program a full range of arm and hand functions in the prosthetic.
This would mean that the user could use the prosthetic almost as seamlessly as if it was their own arm.
The team then encoded specific motor neuron signals as commands into the design of the prosthetic. They then connected a sensor patch on the muscle that had been operated on as part the re-routing procedure, which was connected to the prosthetic. The amputees worked with physiotherapists so they could learn how to control the device by thinking about specific phantom arm and hand commands.
This research has taken the team to the end of the proof of concept stage with laboratory tests. The next step will involve extensive clinical trials with a much wider cross section of volunteers so that the technology can be made more robust.