Researchers at the UCLA Samueli School of Engineering have demonstrated that deep learning, a powerful form of artificial intelligence, can discern and enhance microscopic details in photos taken by smartphones. The technique improves the resolution and color details of smartphone images so much that they approach the quality of images from laboratory-grade microscopes.
The advance could help bring high-quality medical diagnostics into resource-poor regions, where people otherwise do not have access to high-end diagnostic technologies. And the technique uses attachments that can be inexpensively produced with a 3-D printer, at less than $100 a piece, versus the thousands of dollars it would cost to buy laboratory-grade equipment that produces images of similar quality.
Cameras on today’s smartphones are designed to photograph people and scenery, not to produce high-resolution microscopic images. So the researchers developed an attachment that can be placed over the smartphone lens to increase the resolution and the visibility of tiny details of the images they take, down to a scale of approximately one millionth of a meter.
But that only solved part of the challenge, because no attachment would be enough to compensate for the difference in quality between smartphone cameras’ image sensors and lenses and those of high-end lab equipment. The new technique compensates for the difference by using artificial intelligence to reproduce the level of resolution and color details needed for a laboratory analysis.
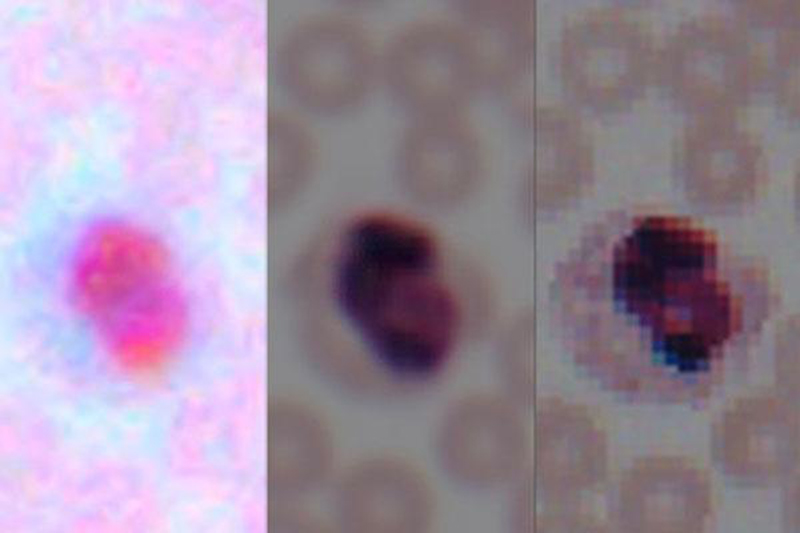
Image of a blood smear from a cell phone camera (left), following enhancement by the algorithm (center), and taken by a lab microscope (right). Photo Credit: Ozcan Research Group/ UCLA
The research was led by Aydogan Ozcan, Chancellor’s Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering and Bioengineering, and Yair Rivenson, a UCLA postdoctoral scholar. Ozcan’s research group has introduced several innovations in mobile microscopy and sensing, and it maintains a particular focus on developing field-portable medical diagnostics and sensors for resource-poor areas.
“Using deep learning, we set out to bridge the gap in image quality between inexpensive mobile phone-based microscopes and gold-standard bench-top microscopes that use high-end lenses,” Ozcan said.
“We believe that our approach is broadly applicable to other low-cost microscopy systems that use, for example, inexpensive lenses or cameras, and could facilitate the replacement of high-end bench-top microscopes with cost-effective, mobile alternatives.”
He added that the new technique could find numerous applications in global health, telemedicine and diagnostics-related applications.
The researchers shot images of lung tissue samples, blood and Pap smears, first using a standard laboratory-grade microscope, and then with a smartphone with the 3D-printed microscope attachment. The researchers then fed the pairs of corresponding images into a computer system that “learns” how to rapidly enhance the mobile phone images. The process relies on a deep-learning-based computer code, which was developed by the UCLA researchers.
To see if their technique would work on other types of lower-quality images, the researchers used deep learning to successfully perform similar transformations with images that had lost some detail because they were compressed for either faster transmission over a computer network or more efficient storage.


