Sometimes when you’re invested in a project you fail to notice things that turn out to be significant.
Researchers in the Rice lab of chemist and bioengineer Jeffrey Hartgerink had just such an experience with the hydrogels they developed as a synthetic scaffold to deliver drugs and encourage the growth of cells and blood vessels for new tissue.
To do so, they often tested the gels by infusing them before injection with bioactive small molecules, cells or proteins. What they didn’t realize until recently was that the hydrogel itself has significant therapeutic qualities.
The lab reported in the Elsevier journal Biomaterials that a particular hydrogel, a self-assembling multidomain peptide (MDP) with the amino acid sequence K2(SL)6K2, is indeed bioactive.
Once Hartgerink and his team started to investigate the phenomenon, they found that even without additives their MDP is rapidly infiltrated by host cells, provokes a temporary inflammatory response, does not develop a fibrous capsule, supports the infiltration of a mature vascular network and recruits nerve fibers.
“We were surprised to find this strong effect in what we had previously considered to be a control peptide,” Hartgerink said. “As it turned out, the inherent structure and chemistry of this peptide, despite being quite simple, results in a strong biological response.”
The hydrogel, which can be delivered through a syringe, is designed to degrade over six weeks and leave behind healthy tissue. Because the peptides are designed from the bottom up to mimic their natural counterparts, the lab found they create an optimal environment for the body’s own systems to encourage healing.
The researchers reported the natural inflammatory response when a foreign substance like a hydrogel is introduced into a system and draws cells that secrete proteins involved in cellular infiltration, scaffold degradation, vascularization and innervation. Tests on injected hydrogel showed a “statistically significant” increase in the presence of cytokines known to provoke an inflammatory response, as well as an increase in anti-inflammatory agents, both of which remained steady after day three and through two weeks.
That, Hartgerink said, indicates the hydrogel appears to harness the body’s innate capacity to heal as it transitions from a pro-inflammatory to a pro-healing environment.
“As we eventually discovered, this exceptional peptide allows the body to carry out healing on its own, but with a significant boost,” he said. “We believe the key step is the initial, and very rapid, cell infiltration. Once these cells are on location, they produce everything they need for an impressive regenerative response, including angiogenesis and neurogenesis.”
Hartgerink said the lab is pursuing application of the peptide for wound-healing in diabetic ulcers.
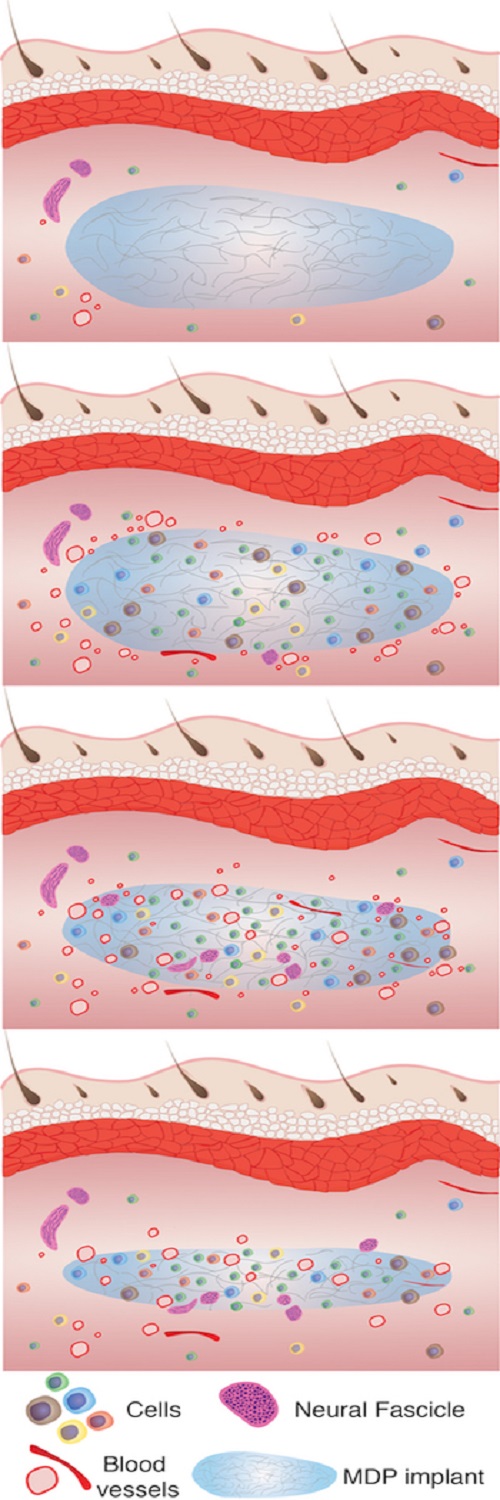
An illustration shows how over six weeks, from top to bottom, a hydrogel developed at Rice University aids tissue remodeling. The process begins with cell infiltration followed by vascularization, innervation and slow degradation of the hydrogel as it is replaced by healthy tissue. Credit: Hartgerink Research Group