Propelling surgical innovation to the next stage, product design and development firm Cambridge Consultants is showcasing Axsis, one of the smallest known robots for surgical use. With an external body the size of a soda can and instruments only 1.8 millimeters in diameter, Axsis provides a glimpse into the future of surgical robotics.
The technology demonstrator uses cataract surgery as an example of a procedure that could benefit from miniature robotics. But Axsis shows the potential for increased precision, minimally invasive access and highly accurate navigation for a wide variety of clinical procedures that cannot be carried out with current surgical robots.
Traditional surgical robots are large by design, stemming from the need to control long, straight instruments that pass through small holes into the patient. The need for systems to be physically large is heightened by the forces they need to exert on the body during surgery, the requirement to adapt to multiple configurations and the degrees of freedom needed to effectively operate them.
In its prototype, Cambridge Consultants has demonstrated that — by using flexible instead of straight instruments — novel motor and control configurations can be used, allowing the overall size of the robot to be reduced significantly, and eliminating the need for a large range of motion outside the body. With the right instrument design, the outer diameter of the minimally invasive access point can also be reduced.
Robotics is already transforming surgery. But Axsis shows how the next wave of miniature systems can revolutionise procedures that require very small and precise movements to access complex or obstructed structures within the body. A smaller robot allows for surgeons and doctors to work with multiple types of tools, and to get closer to the patient without the barrier of large equipment. It also makes procedures less invasive, by enabling surgeons to create much smaller incisions.
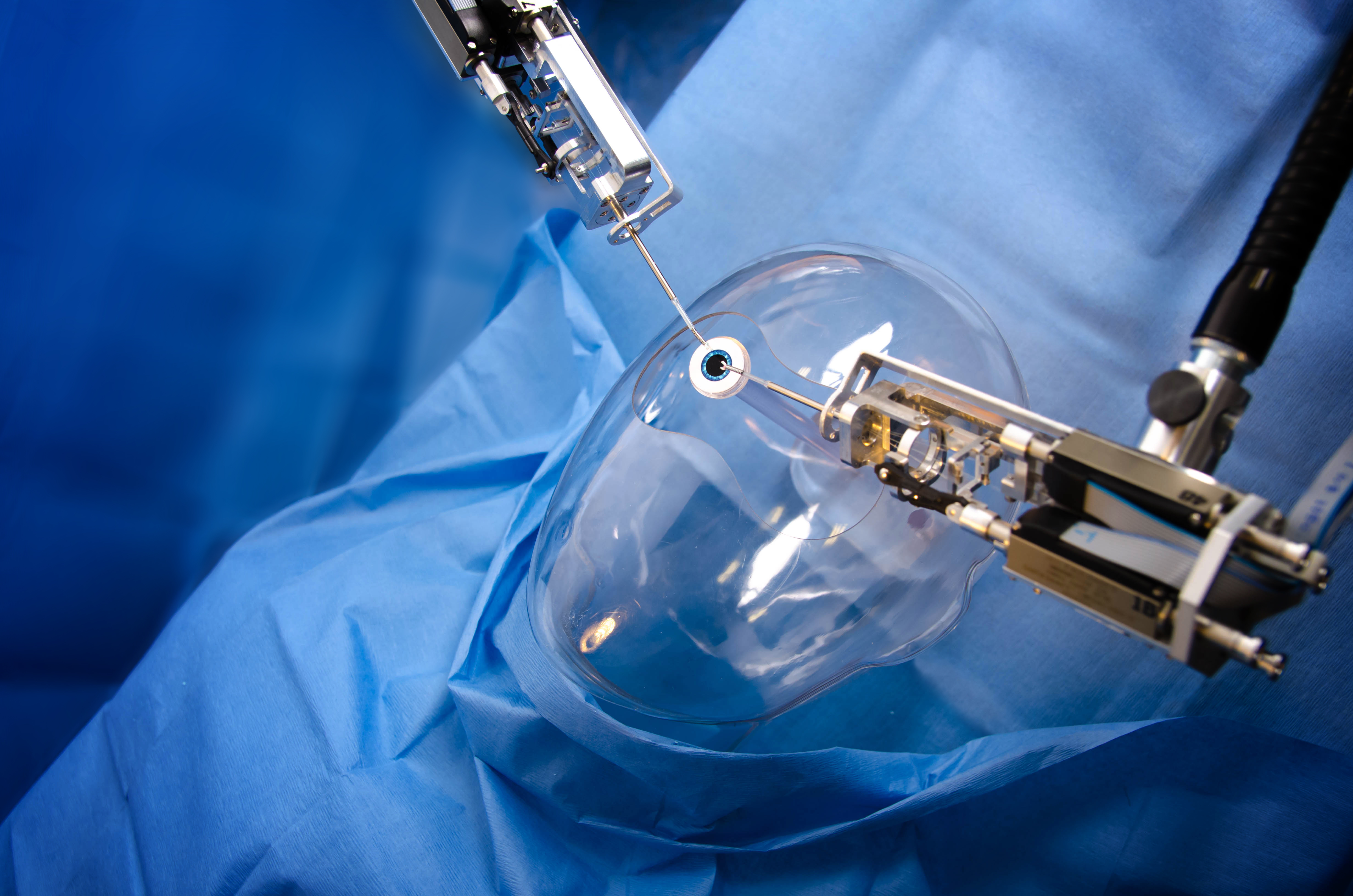
(Image credit: Cambridge Consultants)
“This level of innovation in surgical robotics has the potential to significantly enhance medical treatments and procedures for surgeons and patients alike,” says Chris Wagner, head of advanced surgical systems at Cambridge Consultants. “Take cataract surgery, for example. It is performed by hand, under a microscope, with tools that are about two millimeters in diameter. It’s the world’s most common surgery, yet there are still critical complications that can result due to the small size and delicate nature of the eye, and the experience and skill of the surgeon. This is where the traditional benefits of robotics — such as motion scaling and minimally invasive access — can help. If we can build robots at this size scale, surgeons of all levels of experience can benefit, improving procedure outcomes and allowing more facilities to offer cataract procedures.”
Along with cataract surgery, Axsis demonstrates how the novel system design could improve the way medical professionals approach a variety of other procedures that require a high level of precision and minimally invasive access. From early intervention procedures for cancer, to expanding the reach of natural orifice surgery for oesophageal and gastrointestinal tract procedures, the high precision, control, and access offered by accurate and flexible systems like Axsis can enable surgical outcomes not possible today. Beyond that, Axsis could allow for robotics to be used in procedures that are currently only performed by hand, such as the placement of certain neurostimulation implants.
By creating space efficiency within the operating theatre, Axsis’s small size also promises significant cost savings and lowers the barrier to entry for less experienced robotic surgeons and smaller hospitals, as robotic tools can be swapped in and out as needed. This improves hospital operations while opening up greater access for patients.
A leader in product development, with similar robotics innovations across multiple industries including industrial, agricultural and consumer technologies, Cambridge Consultants has combined a variety of skills and expertise in precision mechanism design, electronics, motion control, industrial design, and human factors to develop Axsis.
“Axsis proves that it is not only possible to create surgical robots that are smaller than ever before, but also to target surgical procedures with robotics that were previously out of reach,” Wagner says.




