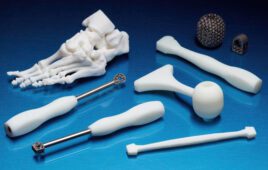
[Image from Kaleidoscope Innovation]
What is an FDM printer?
An FDM (fused deposition modeling) printer is a 3D printer that is often used in early concept development and prototyping for medical device design. FDM refers to how the 3D model is formed. The material (molten plastic) is deposited by a three-axis system in single layers, and multiple layers fuse together to form the 3D model.
How does an FDM printer work?
The process begins with a 3D CAD (computer-aided design) model. Slicing software divides the digital model into numerous slices (layers) and outputs a G-code file for the printer. The FDM printer heats solid plastic filament, and melts and extrudes it from a nozzle — layer upon layer — onto a build tray to form the 3D object. Each layer can be 0.1mm to 0.5mm thick based on the desired resolution.
What are the most common materials used in FDM printers?
The two most common materials in FDM printing are ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) and PLA (polylactic acid). Both are inexpensive and available in a variety of colors.
- ABS, a common household plastic, offers good strength and thermal characteristics, but requires good ventilation as it emits strong odors. It requires a heated build platform to avoid warping.
- PLA offers great surface quality, is one of the easiest materials to print and is also biodegradable but lacks impact strength.
Higher-grade FDM printers can print engineering and higher performance materials including Nylon, TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane), and PET (polyethylene terephthalate) or PETG (polyethylene terephthalate glycol). Frequently used in disposable plastic bottles, PET can be used for pieces that come in contact with food and it does not release odors when printing.
How are FDM printers used?
Medical device designers and engineers often use FDM printers in early concept exploration and medium fidelity prototyping stages.
- Early concept exploration stage: FDM printing allows users to easily print multiple concepts to examine form and fit of the actual piece before pursuing detailed features.
- Medium fidelity prototyping stage: For testing or for prototypes that resemble actual production parts, users often print at medium fidelity. This resolution uses thin 0.1mm layers. This option is ideal for obtaining feedback on feel and performance.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of FDM printers?
Advantages: The most significant advantage that FDM printers offer is the low cost to purchase and operate. Because they are popular in the consumer market, low-end FDM printer models start at $150. FDM printers are easy to operate and offer fast concept to prototype lead time.
Disadvantages: FDM printers do not offer the high quality, dimensional accuracy or reliable operation that some other 3D printers offer. Reliability can be an issue with failed parts or clogs in flowing plastic. FDM is not the best choice for printing parts that need to be “close to perfection.”
What size 3D models do FDM printers build?
In general, the average-size FDM printer can print models approximately 120 mm x 120 mm x 200 mm while some printers can print as large as 500 mm x 500 mm x 500 mm.
Pulkit Verma is a design engineer at Kaleidoscope Innovation in Cincinnati, with a focus on product design. Prior to earning his master’s degree in mechanical engineering, Verma studied product design and intellectual property rights. He has experience working at a law firm in New Delhi, India, where he provided technology-focused legal support to global clients.