
Medical nitinol processing turns nitinol rods into tubes that can be cut to make stents like these — one compressed and the other expanded. [Photo by Zarathustra via Adobe Stock]
We previously covered nitinol’s journey from the earth’s crust through high-temperature melting crucibles and forging operations to create nitinol ingots and then smaller, more workable shapes such as rods and plates.
But turning those into wires, coils, tubes and sheets can be challenging due to the same superelastic and shape memory properties that make nitinol so appealing for a variety of advanced medtech applications.
Making nitinol wire and coils for medical devices
To create nitinol wire, a processor will pull lubricated nitinol rod through diamond-coated drawing dies to elongate the material and reduce its diameter to the desired size. Nitinol coils are made the same way, but spooled to form one long continuous wire instead of cutting it into shorter lengths of wire.

MicroVention’s Woven EndoBridge (WEB)
aneurysm embolization system [Image courtesy of MicroVention]
Annealing is a heating and cooling process before and after passes to remove internal stresses in the nitinol that could later cause device fatigue or durability problems. Nitinol annealing takes the metal’s temperature up to 600-800°C and holds it there for a period of treatment between passes.
Nitinol wire can be drawn down to diameters thinner than a human hair. Such a reduction takes hundreds of draw passes, resulting in an ultra-fine wire. Dozens of those wires could be braided together to reinforce catheters, for example, or woven to create a mesh basket for embolization in aneurysm patients.
Making nitinol tubes for medical devices
Nitinol tubes can be used for catheters, guidewires, stents and needles.
To create a nitinol tube, a processor will take a rod and gun drill to form a cavity down the center. This gun-drilling process — named after the deep hole drills used to form the barrel of a gun — creates a thick-walled tube hollow.
That tube hollow will then go through multiple drawing steps with dies to stretch the hollow and form a tube. A mandrel inside the tube maintains the inner diameter, while the elongation process reduces the outer diameter and tube thickness to the desired dimensions.
Making nitinol sheets for medical devices
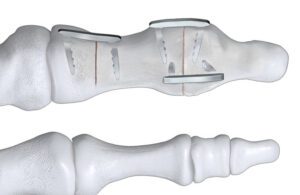
Paragon 28’s Jaws nitinol staple system [Image courtesy of Paragon 28]
Those plates go through rolling mills where hydraulic presses with hardened steel rollers compress the plates and make them thinner and thinner, down to the desired thickness.
Nitinol sheets can be stamped or cut with water or lasers to create the desired pattern or shape.
Next in nitinol
Once nitinol is in the form of wires, coils, tubes and sheets, there are a few more steps for medical device manufacturers to get to a finished component or device. Our next article covers nitinol machining, shape-setting and finishing.
More about medical nitinol manufacturing and devices:
- What is nitinol and where is it used?
- Medical nitinol manufacturing: How this nickel-titanium alloy is made for medical devices
- How Medtronic uses nitinol to improve the structure and effectiveness of heart devices
- How J&J Medtech’s Cerenovus Embotrap stent retriever thrombectomy treats ischemic strokes
- Why Affera’s cardiac ablation technology is worth $1B to Medtronic
- After recall and relaunch, Medtronic wants to go global with its Harmony valve
- Heart failure startup aims for nitinol shape memory breakthrough
This post was published in August 2023 and updated in March 2024.




